E melodic minor scale notes 189754-E melodic minor scale notes
The harmonic minor scale is so called because in tonal music of the common practice period (from approximately 1600 to approximately 1900) chords or harmonies are derived from it more than from the natural minor scale or the melodic minor scale The augmented second between its sixth degree and its raised seventh degree (the "leading tone"), traditionally considered undesirable in melodicDescending E, D, C, B, A, G, F♯The reason is that chords built on melodic minor scale notes don't tend to work so well together This doesn't necessarily mean they're unusable and it's worth noting the chord differences between the minor scales because minor keys are often made from a combination of the minor scale variations

Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Key Signature
E melodic minor scale notes
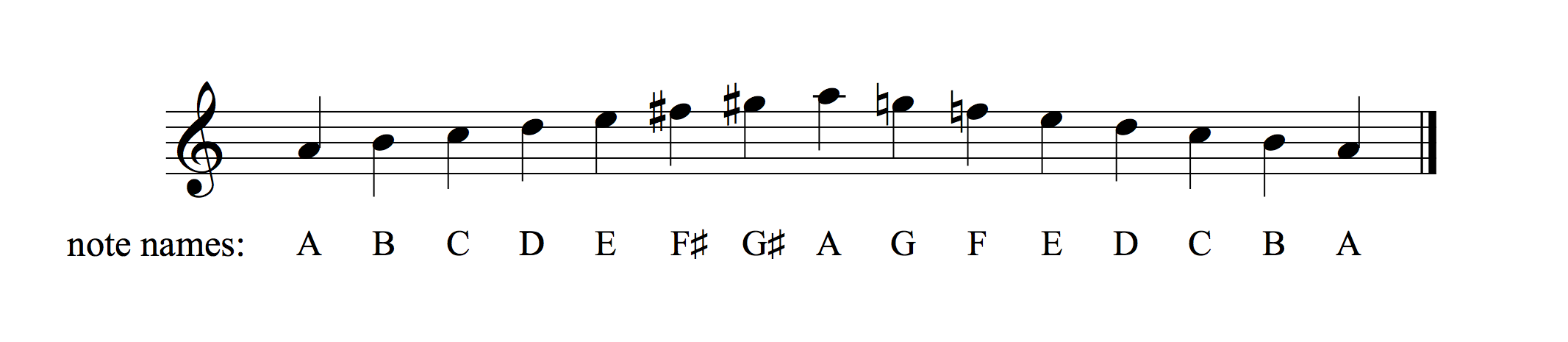
E melodic minor scale notes-Notes in the E melodic minor scale Ascending E, F♯, G, A, B, C♯, D♯Just to have a reference I am demonstrating everything using this position of the Ab melodic minor scale or in this case G altered The G altered scale contains the notes G Ab B Db Eb F In example 3 I have taken each of these notes and let it resolve to a note on a C major chord, so Ab resolves to G, Eb to E or D etc etc


Why The Ascending Form Of The Melodic Minor Scale Differs From Its Descending Form Hear And Play Music Learning Center
In C, that would be C D E G A A melodic minor pentatonic can be thought of as the same numbered tones from the melodic minor scale For C minor, those notes would be C D Eb G A Since this scale is just a subset of the melodic minor scale, we could use it anywhere we might use a melodic minor scale For example, C melodic minor pentatonic could be used over Cm , Cm6 or Cm(maj7) and its extensionsBig list of common triads and four note chords of the scale E Melodic MinorA major pentatonic scale can be thought of as tones 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 from the standard major scale In C, that would be C D E G A A melodic minor pentatonic can be thought of as the same numbered tones from the melodic minor scale For C minor, those notes would be C D Eb G A Since this scale is just a subset of the melodic
Natural minor scales share a key signature with a relative major key that has the same diatonic notes For example, the D minor scale is the relative minor of F major The E minor scale is the relative minor of G majorThe E Melodic Minor scale consists of seven notes These can be described as intervals, as seminotes or steps on the guitar fingerboard, written as 2 1 2 2 2 2 1 from the first note to the next octave This scale has an unusual aspect it ascends as described above but descends as the Natural MinorPentatonic scale in Debussy's Voiles, Preludes, Book I, no 2, mm 43–45 Play (help · info) A pentatonic scale is a musical scale with five notes per octave, in contrast to the heptatonic scale, which has seven notes per octave (such as the major scale and minor scale) Pentatonic scales were developed independently by many ancient civilizations and are still used in various musical
E Melodic Minor Scale 3 Notes Per String Fretboard Diagrams Pentatonic Scale Fluency available from Amazon Pentatonic Scale Fluency Available on Kindle and Paperback Master the minor pentatonic scale using the whole fretboard If you are stuck in the pentatonic box then this is the way out of it Learn how to play up and down the neck withE Melodic Minor Scale 3 Notes Per String Fretboard Diagrams Pentatonic Scale Fluency available from Amazon Pentatonic Scale Fluency Available on Kindle and Paperback Master the minor pentatonic scale using the whole fretboard If you are stuck in the pentatonic box then this is the way out of it Learn how to play up and down the neck withHere are the E Minor Scales the natural minor scale, the melodic minor scale, and the harmonic minor scale Fingerings are included Learn the scales ascending and descending First, try one octave, and then try two octaves (Eventually, you should be able to play each scale with both hands, ascending and descending, four octaves)



E Melodic Minor Scale Piano Keys And Guitar Tab



Why Are There 3 Different Minor Scales Free Online Piano Lessons The Note Pianote Lisa Witt
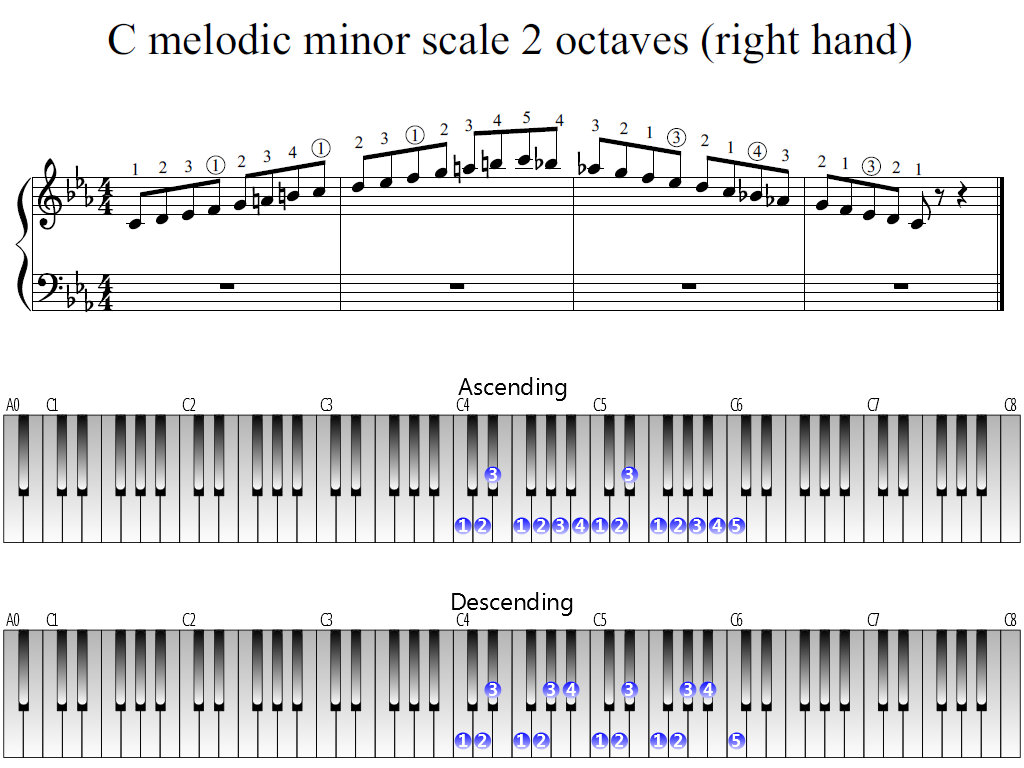
Scale Formula Ascending W, H, W, W, WWe can also use this scale over other chords that are derived from the A melodic minor scale and its modes For example we can build Am(Maj9) from the A melodic minor scale We know that E major b6 pentatonic will work perfectly over this A minor major 9th chord Notes A, C, G#, B Intervals R – b3 – 7 – 9 A Minor Major 9 ChordMelodic Minor Scale The most difficult of these three minor scales is the melodic minor scale The formula for the melodic minor scale is played with the 6th and 7th notes each going up an additional halfstep as the notes ascend Beginning with the first (or root) note of a scale, you'd use this formula to construct the melodic minor scale



Melodic Minor Scale



Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange
Let me repeat this important point e ven though the normal way of playing the Descending Melodic Minor Scale is to play the notes of the Natural Minor Scale, please note that some musicians might choose to play the notes of the Ascending Melodic Minor Scale for the Descending Melodic Minor ScalePS Here are the melodic minor scales in all twelve keys C melodic minor scale C# melodicNotes in the E melodic minor scale Ascending E, F♯, G, A, B, C♯, D♯



A Beginner S Guide To Keys In Music The Cello Companion



Escalas Trombon
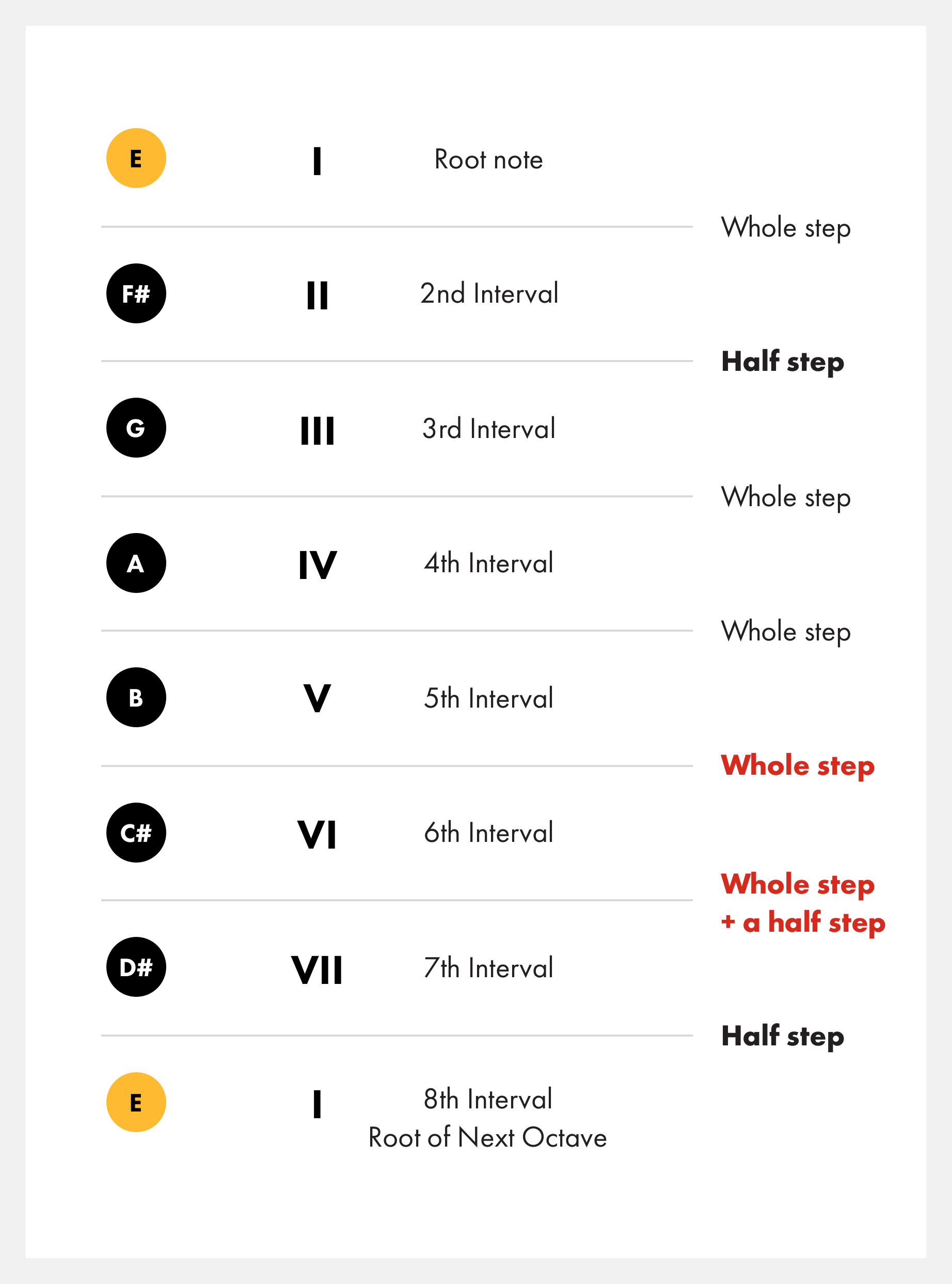
Construction o'f the Melodic Minor 1 Scale The melodic minor scale can be most easily seen as a variation of the natural minor scale Simply raising the sixth and seventh degrees of the natural minor scale yields the melodic minor scale Building this scale from a tonic of C, we get these notes c 1 1/2 step / \_ I D Ev 2 ~3 F 4 G 5 A 6 1/2 step / " B C 7 1 (8) The improviser should be able toThe red dots indicate a root note and the black dots indicate a note in the scale All of the root notes are "E" because this is the E Melodic Minor Scale The E Melodic Minor Scale can be divided into patterns Any Melodic Minor Scale can be divided into patterns Roll your mouse over the pattern number below to see what the pattern looks likeE Melodic Minor Scale Tonic The 1st note of the E melodic minor scale is E Major 2nd The 2nd note of the scale is F# Minor 3rd The 3rd note of the scale is G Perfect 4th The 4th note of the scale is A Perfect 5th The 5th note of the scale is B Major 6th The 6th note of the scale is C#
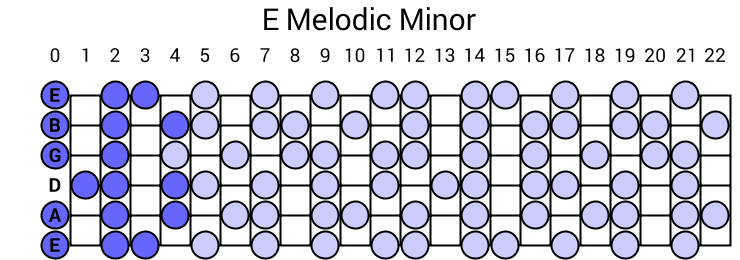


E Melodic Minor Scale


How To Use The Melodic Minor Scale
E melodic minor Guitar Scales Chart C C# Db D D# Eb E F F# Gb G G# Ab A A# B Show All E Scales Hide Scales List E Major E Major pentatonic E Minor pentatonic E Dorian E Phrygian E Lydian E Mixolydian E Aeolian E Locrian E Blues E Harmonic Minor E Melodic Minor E Whole ToneE Minor scale for bass guitar presented by diagram The E Minor displayed as fingerboard diagram for bass The notes are marked in blue color, root notes are the darker ones The oneoctave pattern starts on the 3rd string, 7th fretThe Natural Minor This is the minor scale in its most basic form Every major scale has a 'relative' minor G major has one sharp (F#) Its relative minor is Em, which also has one sharp (F#) The notes of Em are exactly the same as G major, just starting on E This is the 'natural' minor The scale is played according to its key


Music Crash Courses



Higher And Advanced Higher Music Help The Melodic Minor Scale
Piano Scales Chart C C# Db D D# Eb E F F# Gb G G# Ab A A# B Show All E Scales Hide Scales List E Major E Major pentatonic E Minor pentatonic E Dorian E Phrygian E Lydian E Mixolydian E Aeolian E Locrian E Blues E Harmonic Minor E Melodic MinorMelodic minor scales derive from the sevennote natural minor scale, which is characterized by a minor third scale degree (or flat third), a minor sixth scale degree (or flat sixth), and a minor seventh scale degree (or flat seventh)Learn how to play the Melodic Minor guitar scale with guitar tabs and neck diagrams all along the fretboard This scale is made up of the Root, Major Second, Minor Third, Perfect Fourth, Perfect Fifth, Major Sixth, and Major Seventh The notes of this scale are C, D, Eb, F, G, A, and B


Untitled


Q Tbn And9gcqkvw Eb3qf45bsandm Kimpn8dzndgl1wshw7gjppc Cwgpzpd Usqp Cau
E melodic minor scale E, F#, G, A, B, C#, D# For more help, here is a downloadable music scale chart and music mode chart combined, including the melodic minor scale All minor scale notes including natural, melodic and harmonic Try our Scale FinderIn modern notation, the key signature for music in a minor key is typically based on the accidentals of the natural minor scale, not on those of the harmonic or melodic minor scales For example, a piece in E minor will have one sharp in its key signature because the E natural minor scale has one sharp (F ♯)The red dots indicate a root note and the black dots indicate a note in the scale All of the root notes are "E" because this is the E Melodic Minor Scale The E Melodic Minor Scale can be divided into patterns Any Melodic Minor Scale can be divided into patterns Roll your mouse over the pattern number below to see what the pattern looks like


Melodic Minor Scale On Guitar Everything You Need To Know



The Ultimate Guide To Minor Keys Musical U
Please note that the 7th degree cannot be called "leading tone" unless it is raised by a semitone with a sharp (or a natural when the 7th degree has a flat in the key signature) The minor scale is one of the diatonic scales, meaning that it is made up of five whole steps and two half steps The sequence is the same for all minor scales one whole step, one half step, two whole steps, one half step, two whole steps (W, H, W, W, H, W, W)The reason is that chords built on melodic minor scale notes don't tend to work so well together This doesn't necessarily mean they're unusable and it's worth noting the chord differences between the minor scales because minor keys are often made from a combination of the minor scale variationsIntroduction As we have already learned, a Mode is a scale created by establishing a new root note within a preexisting scale We are already familiar with the Modes of the Major Scale, but we can create modes from any preexisting scaleIn Jazz, the modes of the melodic minor scale are very widely used



Theory Blog Melodic Minor Scale
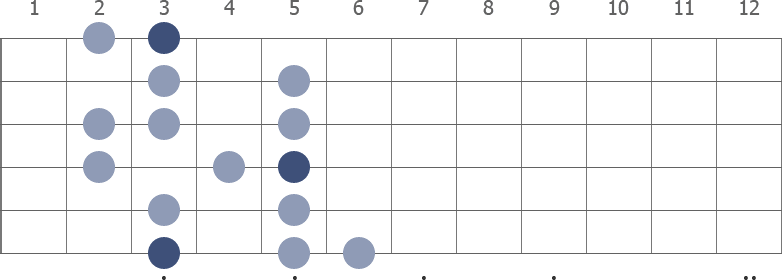


G Melodic Minor Guitar Scale
E harmonic minor scale The Melodic Minor Scale Now onto the third type of minor scale which is the melodic minor Melodic minor scales are quite different from natural and harmonic minors as they use different notes when ascending (going up) and descending (going down)E harmonic minor scale The Melodic Minor Scale Now onto the third type of minor scale which is the melodic minor Melodic minor scales are quite different from natural and harmonic minors as they use different notes when ascending (going up) and descending (going down)Piano Scales Chart C C# Db D D# Eb E F F# Gb G G# Ab A A# B Show All E Scales Hide Scales List E Major E Major pentatonic E Minor pentatonic E Dorian E Phrygian E Lydian E Mixolydian E Aeolian E Locrian E Blues E Harmonic Minor E Melodic Minor
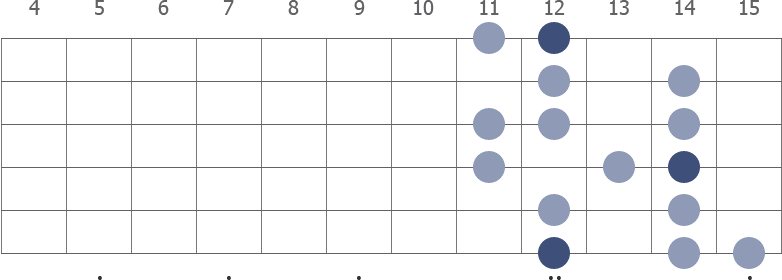


E Melodic Minor Guitar Scale



The Minor Scales Natural Harmonic And Melodic Hello Music Theory
Scale Formula Ascending W, H, W, W, WThe first item on our checklist of altered scale studies is digging into the construction of this commonly used melodic device The altered scale is the 7th mode of the melodic minor scale, which means that it is like playing Ab melodic minor starting from the note GThe altered scale is used to solo over dominant 7th chords, both in major and minor keysThe Melodic Minor Scale is a Major Scale with a flat 3rd (b3) and it's used mostly in it's modal forms of the Altered Scale (Superlocrian) and the funky Lydian Dominan N/A N/A Melodic Minor Pattern 1 Because the only difference between the Melodic Minor and The Major Scale is one note the flat 3 the scale patterns are also similar


Melodic Minor Scale On Guitar Everything You Need To Know



4 4 Minor Keys And Scales
E melodic minor scale The Solution below shows the E melodic minor scale notes, intervalsThe 1st note of the Eflat melodic minor scale is Eb 2 Ebmaj2nd The 2nd note of theDescending E, D, C, B, A, G, F♯


Melodic Minor Scale Guide For Jazz Guitar Jamie Holroyd Guitar Jamie Holroyd Guitar



The E Minor Scales
Now onto the third type of minor scale which is the melodic minor Melodic minor scales are quite different from natural and harmonic minors as they use different notes when ascending (going up) and descending (going down) Ascending melodic minors use this combination of tones and semitones T – S – T – T – T – T – SA melodic minor scale There are three different types of minor scale the natural minor;Eflat melodic minor scale The Solution below shows the Eb melodic minor scale notes, intervals and scale degrees on the piano, treble clef and bass clef The Lesson steps then describe how to identify the Eflat melodic minor scale note interval positions, choose the note names and scale degree names For a quick summary of this topic, have a look at Melodic minor scale



Melodic Minor Pentatonic Lesson


Http Static1 Squarespace Com Static 521bb4bee4b093a8696f53f1 T 561af3efe4b0ae8c3b9f865f Int1 3s E Natural Melodic And Harmonic Minor Pdf
The melodic minor scale is that minor scale that has a leading note feeling and at the same time is not gapped In another post, you'll discover the relationship between the melodic minor scale and the natural major and minor scales Until then!What Is The Altered Scale?Here are the E Minor Scales the natural minor scale, the melodic minor scale, and the harmonic minor scale Fingerings are included Learn the scales ascending and descending First, try one octave, and then try two octaves (Eventually, you should be able to play each scale with both hands, ascending and descending, four octaves)



Cello Online Scales Two Octave Minor Scales



Study The Minor Scale
Warmup, strengthen and improve your violin playing with Violin Online's free two octave melodic minor violin scales ViolinOnlinecom offers free violin scales, free violin etudes, free violin exercises, and free violin sheet music and online violin instruction for individuals or groups of all ages Review violin technique, strengthen playing with free exercises, print violin, cello and violaMelodic Minor Scales overview (auxiliary notes in descending scale in parentheses) A A, B, C, D, E, F# (F), G# (G), A A#/ , C, Db, Eb, F, G (Ab), A (Ab), B B, C#, D, E, F#, G# (G), A# (A), B C C, D, Eb, F, G, A (Ab), B (), C C#/Db C#, D#, E, F#, G#, A# (A), C (B), C# D D, E, F, G, A, B (), C# (C), D D#/Eb D#, F, F#, G#, A#, C (B), D (C#), D#Something that is important to note about the ascending version of the melodic minor scale, is that it shares exactly 6 unique notes with the major scale and only 5 unique notes with the natural minor scale For example, the ascending melodic minor scale shares the notes A, B, D, E, F#, and G# with the A major scale



Cello Online Scales Two Octave Minor Scales


The Melodic Minor Scale
Each type of minor scale uses a slightly different formula of semitones and tones but they all have that minor third For more info about the types of minor scales check out my post hereThe melodic minor scale was (like the harmonic minor scale) originally derived from the natural minor scale, by raising its 6th and 7th note The natural minor in turn is the Aeolian mode of the major scale 3 semitones higherConstruction o'f the Melodic Minor 1 Scale The melodic minor scale can be most easily seen as a variation of the natural minor scale Simply raising the sixth and seventh degrees of the natural minor scale yields the melodic minor scale Building this scale from a tonic of C, we get these notes c 1 1/2 step / \_ I D Ev 2 ~3 F 4 G 5 A 6 1/2 step / " B C 7 1 (8) The improviser should be able to



E Melodic Minor Scale Free Melodic Minor Scales
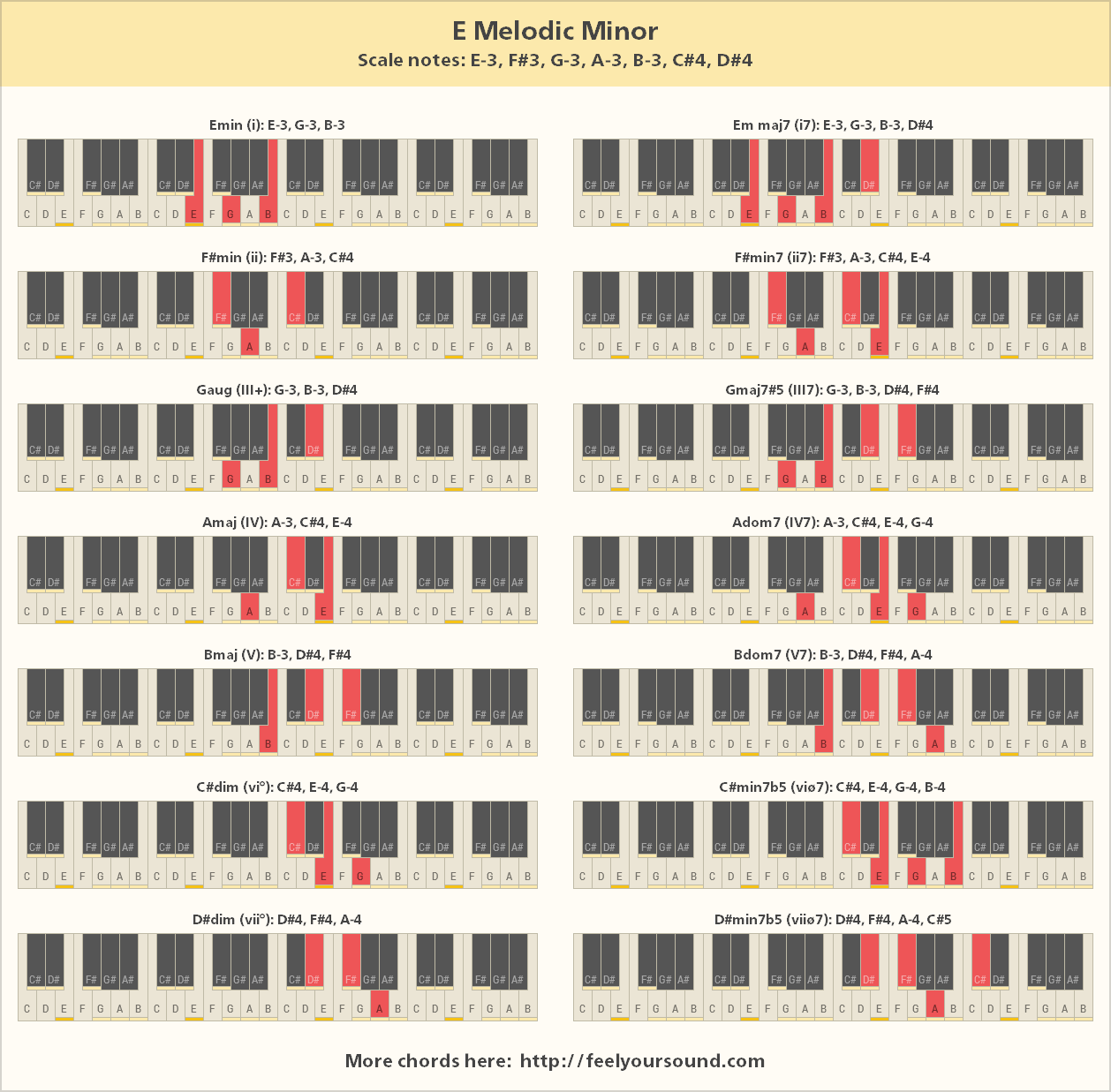


Chords And Scale Notes Of E Melodic Minor
Playing the E minor scale in seventh position requires positioning your hand up to play notes on the seventh, eighth, ninth, and tenth frets as shown in the diagram below 12th Position To play the E minor scale in 12th position, you'll play notes on the 12th, 13th, 14th, and 15th frets as shown in the diagram belowFor example E Phrygian is a minor mode, therefore it should be compared to E Natural Minor and not E Major By doing so, we would find out that the two scales differ from each other by one note F in the Phrygian mode instead of F# which appears on the E Natural Minor scale There is an exception, and that is the Locrian mode



E Melodic Minor Scale Note Information And Scale Diagrams For Guitarists


Harmonic Minor Scale And Chords Natural And Melodic Minor Piano Music Scales



Viola Online Scales Viola Two Octave Minor Scales



Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Scale


The Freakiness Of Melodic Minor The Ethan Hein Blog


The E Minor Scale Three Types How To Form



E Flat Melodic Minor Scale Piano Keys And Guitar Tab



What Makes The Melodic Minor Scale So Melodic Premier Guitar


Jazclass Jazz Scales Lesson Melodic Minor Scale In All Keys


The E Minor Scale Three Types How To Form



Viola Online Scales Viola Two Octave Minor Scales



The Foundations Scale Steps And Scales



Free Piano Exercise 1 Octave Melodic Minor Scales In 12 Keys
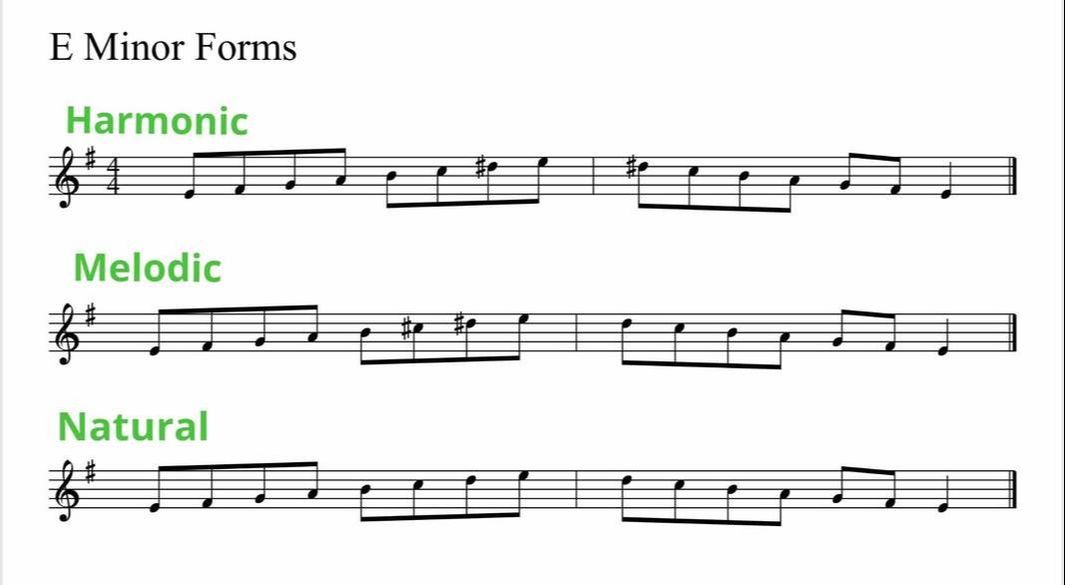



Relative Majors And Minors How To Work Out Minor Scales On The Piano Ruth Pheasant Piano Lessons



Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Scale



Melodic Minor Scale Chords Key And Applications Simplifying Theory



Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Key Signature



Melodic Minor Scale


Untitled



Violin Online Two Octave Melodic Minor Violin Scales



Why Do The Notes Of Melodic Minor Scale Change When You Play It In Descending Order Music Practice Theory Stack Exchange


Major Minor Relationships



The Melodic Minor Scale Scale Music Music Theory Lessons Music Composition



How To Find Use The Melodic Minor Scale On Your Guitar


Scales Clairnote Sn Music Notation
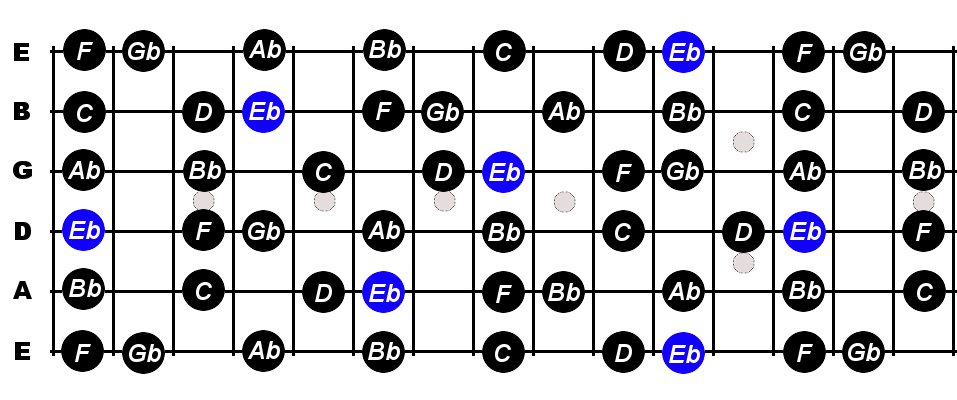


E Flat Melodic Minor Scale For Guitar Constantine Guitars
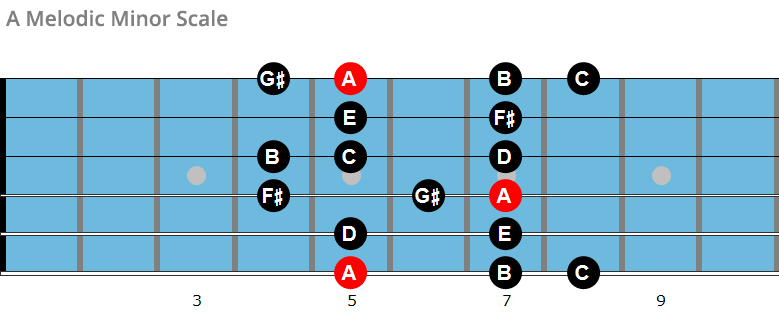


The Melodic Minor Scale And Its Modes



E Melodic Minor Scale Note Information And Scale Diagrams For Guitarists


The Minor Scales And Chords Portland Piano Lab



Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Scale



Melodic Minor Scale For Guitar Gosk


Why The Ascending Form Of The Melodic Minor Scale Differs From Its Descending Form Hear And Play Music Learning Center



Basicmusictheory Com E Melodic Minor Scale


Untitled



Pin On Guitar Scales



Melodic Minor Scale 3 Notes Per String Jens Larsen



Eb Melodic Minor Scale Free Melodic Minor Scales
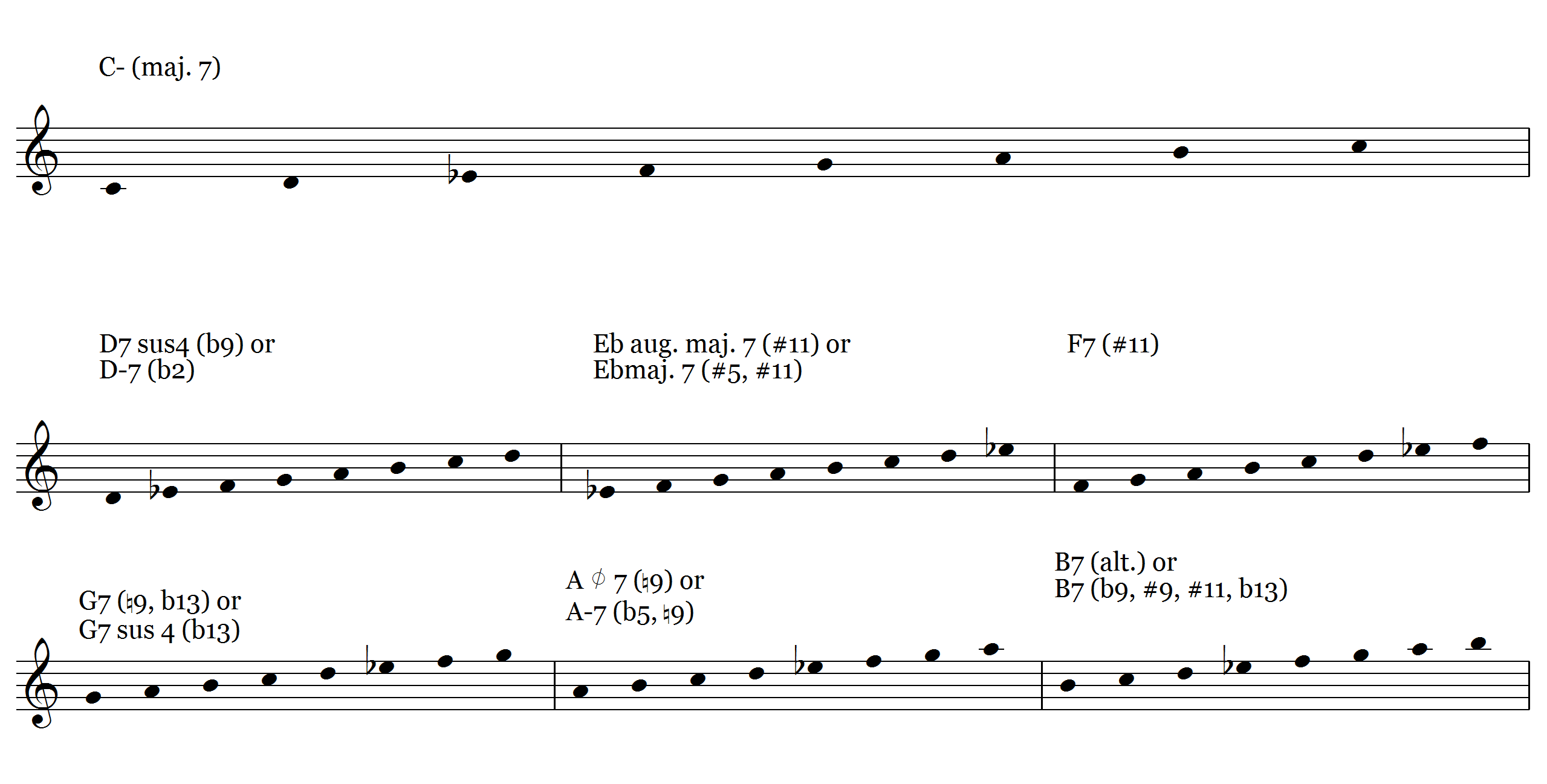


Ljs 86 7 Chords You Can Play The Melodic Minor Scale Over Learn Jazz Standards
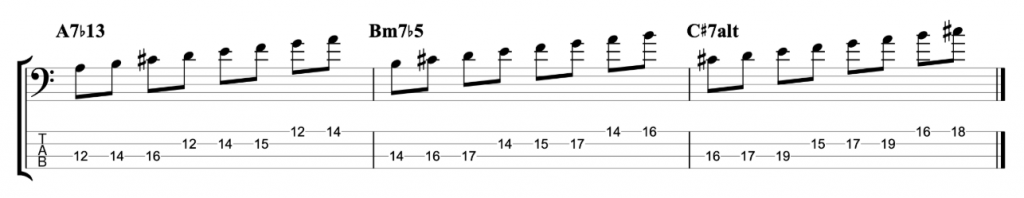


The Modes Of The Melodic Minor Scale Bass Practice Diary 54 Johnny Cox Music



Basicmusictheory Com E Sharp Melodic Minor Scale



4 4 Minor Keys And Scales


The E Minor Scale Three Types How To Form


Why The Ascending Form Of The Melodic Minor Scale Differs From Its Descending Form Hear And Play Music Learning Center
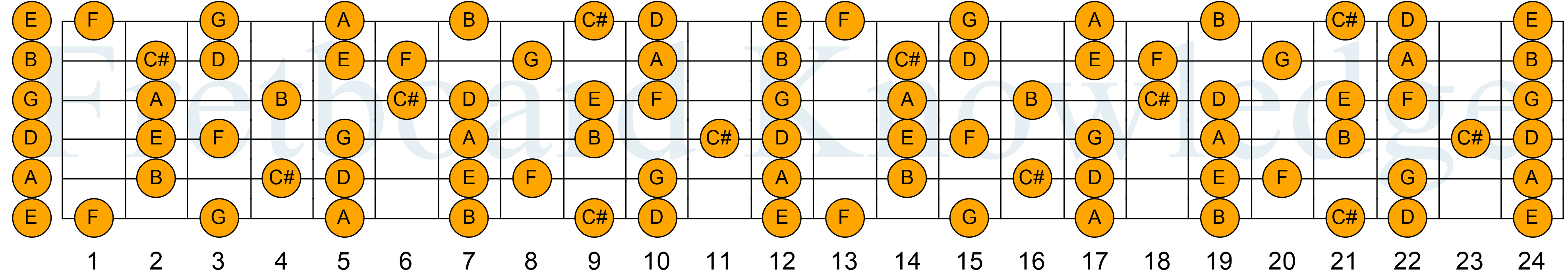


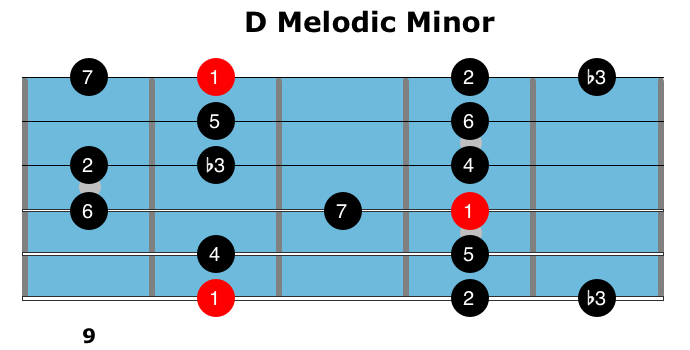
D Melodic Minor Guitar Fretboard Knowledge
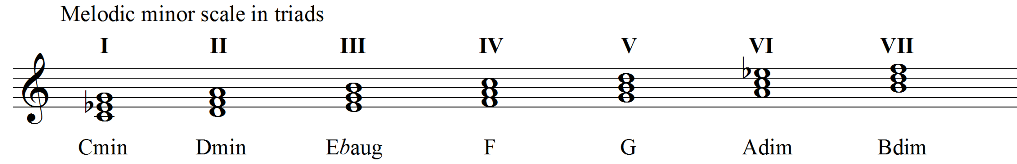


Melodic Minor Scale Harmonization With Guitar Diagrams


Dansm S Guitar Scale Lessons The Melodic Minor Scale


Q Tbn And9gcss J2ksklbyfta61qwvypxyi46nfmky86wesqazepr0pg66sqy Usqp Cau



The Natural Minor Scale Harmonic Minor Scale And Melodic Minor Scale Do Re Mi Studios


1


Melodic Minor Scales The Fundamentals Of Music



The Minor Scales Natural Harmonic And Melodic Hello Music Theory



Music Teachers Page 2 The Cello Companion
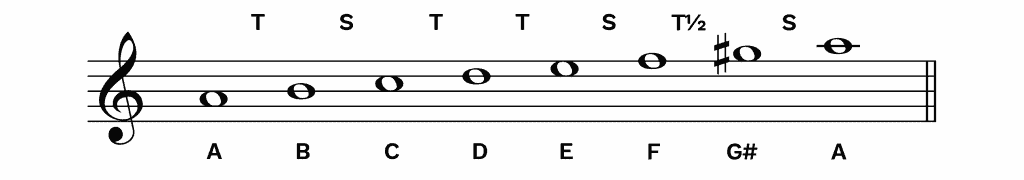


The Minor Scales Natural Harmonic And Melodic Hello Music Theory


Q Tbn And9gcqvhopmmq9znxxfpety46lpekg1adzjvqevhjtckabrrgzfyqkm Usqp Cau


Minor Scales Part 3 Melodic Minors Youtube



Understanding Theory Part 1 Scales Pianist



Why Are There 3 Minor Scales School Of Composition


Music Theory Scales And E Minor Scale



Basicmusictheory Com E Flat Melodic Minor Scale



The Minor Scales Music Theory Academy



Melodic Minor Arpeggios Jens Larsen


Melodic Minor Scales The Fundamentals Of Music
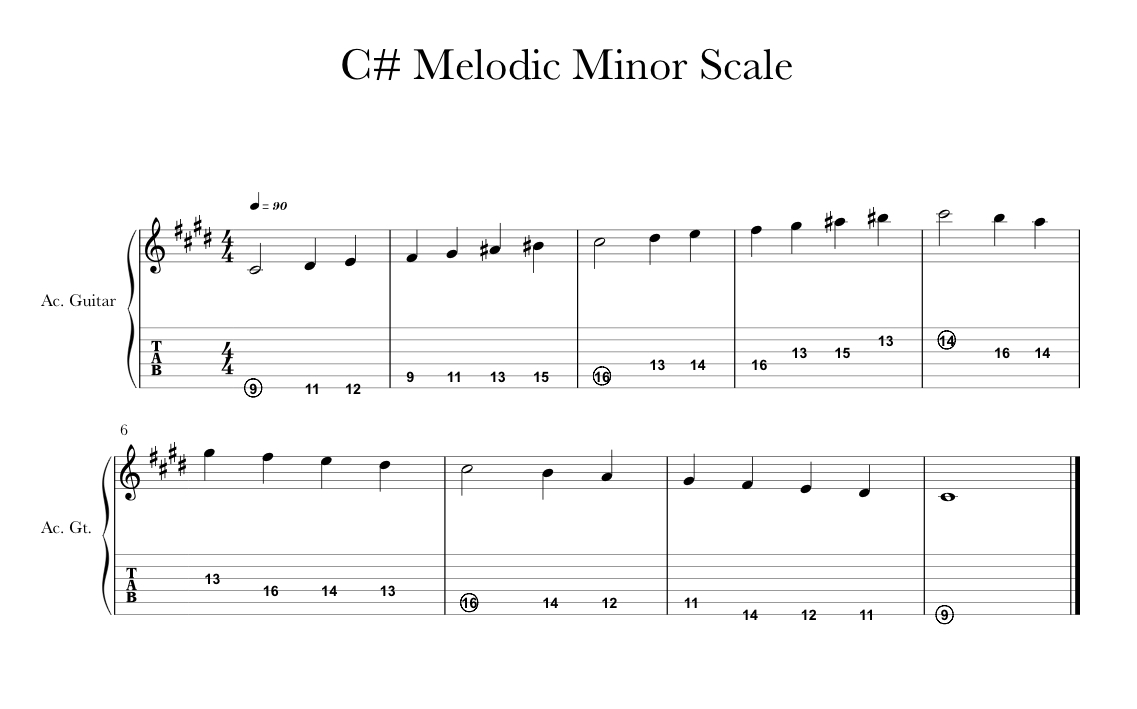


Minor Scales Sabetmusic



E Minor Wikipedia



Melodic Minor Scale Caged Jens Larsen


Learn About Minor Scales On Guitar Fender Play



Why Are There 3 Minor Scales School Of Composition



C Sharp Natural Minor Scale Bass Clef Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Chords Of The Melodic Minor Scale Arthur Fox Music



3 Octave E Melodic Minor Scale Viola Youtube



Chords Of The Melodic Minor Scale Arthur Fox Music


Jazclass Jazz Scales Lesson Melodic Minor Scale In All Keys


The E Minor Scale Three Types How To Form
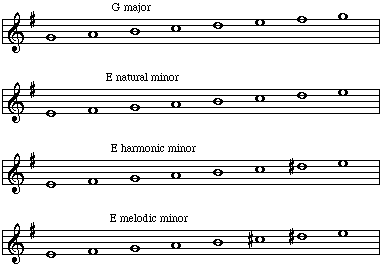


Major Minor Relationships



コメント
コメントを投稿